Medication Warnings
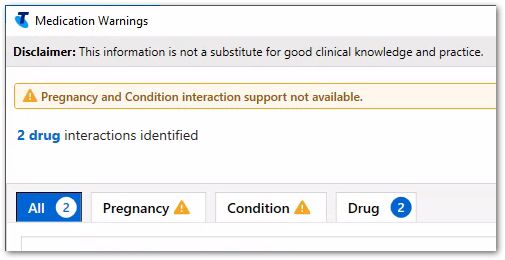
The Medication Warnings window displays drug and adverse reaction warnings, and pregnancy, condition and drug interaction warnings. Use this information to support your prescribing decisions.
This module uses the MIMS databases installed locally or the CDS service.
When you write a prescription, create a medication order or administer and supply a medication, the newly selected drug is checked against the patient's existing clinical items, clinical data and all currently prescribed medications. Medications are treated as current if they have not expired.
- Extemporaneous - extemporaneous preparations are listed
- Reaction - warnings are displayed for medications for which the patient has a recorded adverse reaction
- Pregnancy interactions - any interactions between the active ingredients in the medication and pregnancy are listed
- Condition interactions - if condition interaction support is available at your health service, any interactions between the active ingredients in the medication and the patient's recorded conditions or procedures are listed
- Drug interactions - any interactions between two nominated generic substances are listed
- Warning - any duplication of active
ingredients between medications is displayed in the following order:
- Currently prescribed medications
- Previously stopped medications
To proceed, read the warnings and interactions either on the All tab, where all warnings and interactions are listed, or by warning type on each separate tab, and click Noted.
Extemporaneous
Extemporaneous preparations are listed, but interaction and adverse reaction checks and drug warnings are not provided. Use your clinical knowledge to determine the safety of the preparation.
Reactions
When prescribing, clinicians will receive a reaction warning if prescribing medication which contains a generic component for which a patient has a recorded allergic adverse reaction. If enabled, clinicians will be required to enter their password to proceed with a prescription for which the patient has a recorded allergic adverse reaction, and the action is logged. If the Substance Warning has been applied to the reaction, all generic components of the same substance class will have a warning. Those generic components with cross sensitivities are also included.
Pregnancy interactions
When you add a medication, if a female patient is pregnant, a pregnancy status banner is displayed in the Medication Warnings window and any interactions between the active ingredients in the medication and pregnancy are listed.
You can also check pregnancy interactions later, after you have already prescribed medications.
Interactions are listed in severity order.
Interaction support is available only for clinical items with a valid ICPC-2 PLUS code.
The Pregnancy tab displays a
Condition interactions
If condition interaction support is available at your health service, when you add a medication any clinical item that is a condition or a procedure and has a valid ICPC-2 PLUS code is checked for possible interactions. Any interactions between the active ingredients in the medication and the patient's conditions or procedures are listed. Only condition interactions for the relevant medication route are displayed.
All conditions for a patient are checked, including those that are no longer active.
You can also check condition interactions later, after you have already prescribed medications.
Interactions are listed in severity order.

The Condition tab displays a
Drug interactions
The MIMS database is used to check the documented interactions between two nominated generic substances. When a brand is selected, each generic component (or its allocated class) is compared against every other generic component (both those on the prescription being generated and those on the patient's current medication list) on an individual (paired) basis. When more than two generic substances are prescribed, the database checks the interaction between all possible paired combinations of generics, but cannot provide information about the overall combination.
The compound effect of the interactions arising from the combination of more than two generics cannot be evaluated using this database, because the number of possible permutations and combinations make it impossible to generate full interaction data using current technology. Therefore, the prescribing clinician must assess the combined consequences of all the displayed interactions for each patient.
Severity ratings
Drug interactions are listed from the most severe with the best documentation to the least severe.
| MIMS Severities | Example |
|---|---|
| Severe (1): The interaction between these medications may be life-threatening or may cause permanent damage. These medications are not usually used concurrently; medical intervention may be required. |  |
| Moderate (2): These medications may interact, resulting in the potential deterioration of the patient's condition. The patient should be monitored for possible manifestations of the interaction. Medical intervention or a change in therapy may be required. |  |
| Minor (3): Clinical effects of the interaction are limited and may be bothersome but would not usually require a major change to therapy. The patient should be monitored for possible manifestations of the interaction. |  |
| Caution (4): The interaction may occur based on the mechanism of action of the co-administered medicines. Be alert for increased or decreased effect, depending on the combination of medicines. |  |
| Not Clinically Significant (5): The interaction may occur, but the outcome is not clinically significant. |  |
| Not Established (6): The interaction may theoretically occur due to its pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics. There have not been any established reports of the interaction. |  |
Documentation levels
- Well established - there have been several published reports of this interaction. The pharmacological explanation of why the interaction occurs is well documented and understood. There are usually controlled studies that have established that the interaction exists.
- Good - although controlled studies may not have been performed, several case reports have been documented and other data strongly suggests this interaction exists.
- Limited - few reports of this interaction exist. These few reports usually consist of limited case reports where clinically sound justification of the interaction is found.
- Not established - the interaction may have occurred with other medicines within the same class, or there is a theoretical possibility that the interaction exists.
Warnings
Conflicts where common generic substances exist in multiple drugs currently being prescribed are listed (to advise against overdose). Warnings are also displayed where the same generic substance has been prescribed to the patient in the past, then stopped for a reason.
